6 Benefits of Sustainably Harvesting Timber and Selective Timber Harvests.
1. Timber harvests promote forest regeneration.
Sustainably harvesting timber promotes regeneration (the process by which new trees and other plants are established) by freeing of space in the canopy and understory and reducing the effects of competition. The newly freed space in the understory, having greater access to sunlight, water, and nutrients, encourages new trees and other native plants to seed in, take root, and grow.
2. Timber harvesting promotes biodiversity of plants and animals.
Timber harvests can be utilized to manipulate the overall composition and age class of a timber stand by selectively and strategically marking trees for harvest. Timber stands containing a wide variety of native tree species at multiple age classes, are able to provide habitat for a wider variety of wildlife species.
3. Timber harvests enhance/improve wildlife habitat.
Fallen, dead tree remains, known as course woody debris (CWD), left behind following harvesting operations enhance habitat by providing additional sources of food, cover, and shelter for wildlife. A variety of insects, a vital source of food for many wildlife species, can be found in downed and/or decaying CWD. Some small mammals, reptiles, and amphibians may also live in and/or under CWD. Downed tree canopies, branches, and brush piles also provide protection and cover to a variety of wildlife species.
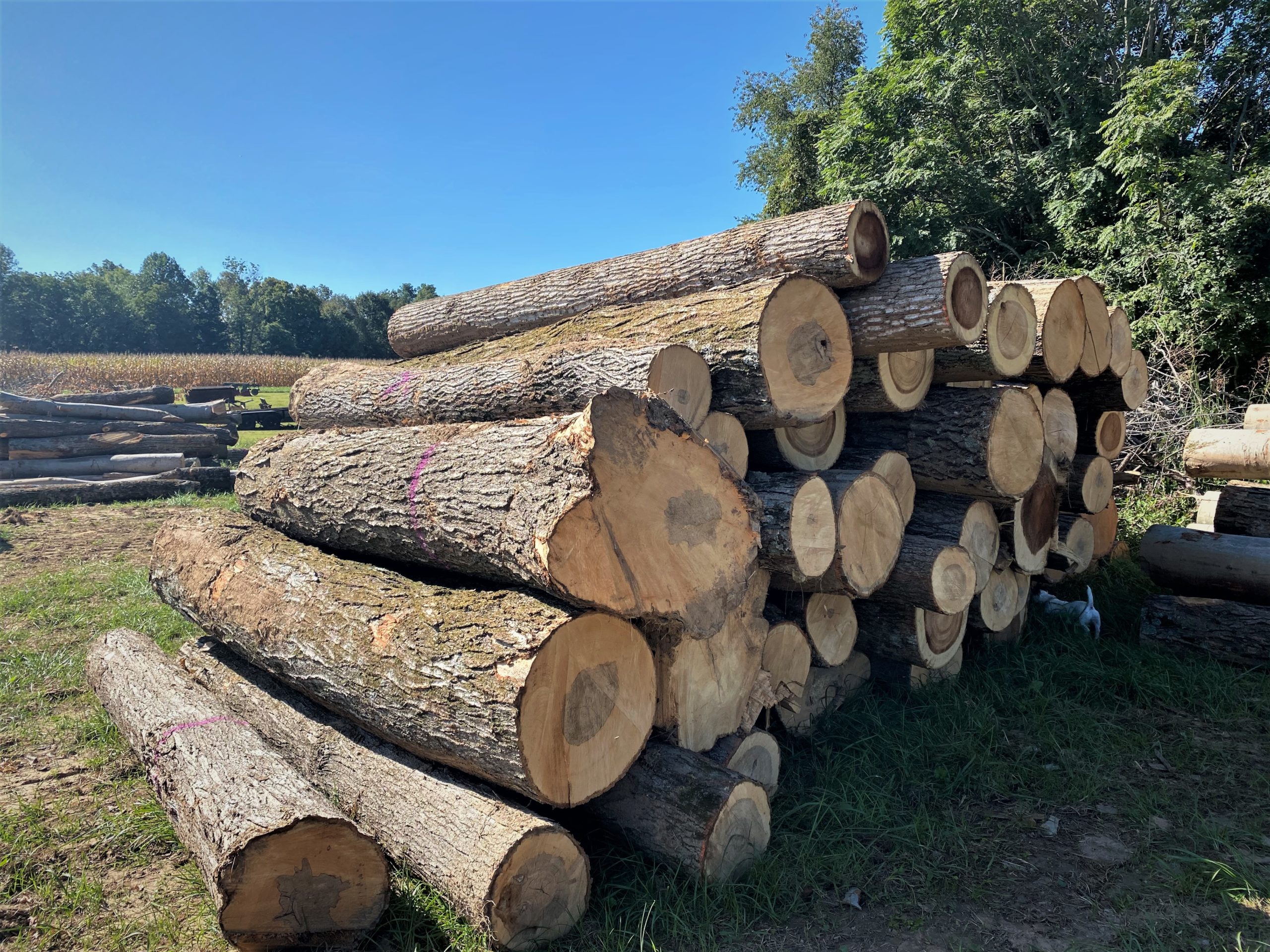
4. Timber harvesting improves timber quality and value.
If trees are selectively marked and the harvest is conducted sustainably and ethically, timber may be able to be harvested as often as every 10 to 15 years. This results in a continual source of income as well as continued forest maintenance, benefitting the overall health and productivity of the timber stand. Timber harvests may also be used as a forest improvement practice to reduce stocking levels and alter species composition of the stand, as well as remove any poor-formed, unhealthy, or over-mature trees.
5. Timber harvests promote forest productivity, efficiency, and regeneration.
Overstocked, dense timber stands grow less productively and efficiently due to the effects of increased competition for space, water, sunlight, and other vital nutrients. Thinning a stand by the use of a sustainable timber harvest allows the trees left standing post-harvest better access to vital nutrients and space, allowing them to grow faster, more productively, and efficiently. The freed space in the canopy also promotes native regeneration in the understory.
6. Timber harvesting provides the wood necessary for a variety of consumer products.
The wood and paper products we use every day rely on the continued harvest of timber. Although the demand for and the collection of timber has grown over the years, the United States is more forested today than it was 50 years ago as a result of research advancements and ongoing education regarding sustainable forest management practices.


Click here to learn more about our timber harvesting services.
Other sources of information: